hashtable&concurrenthashmap1.7&1.8 总结
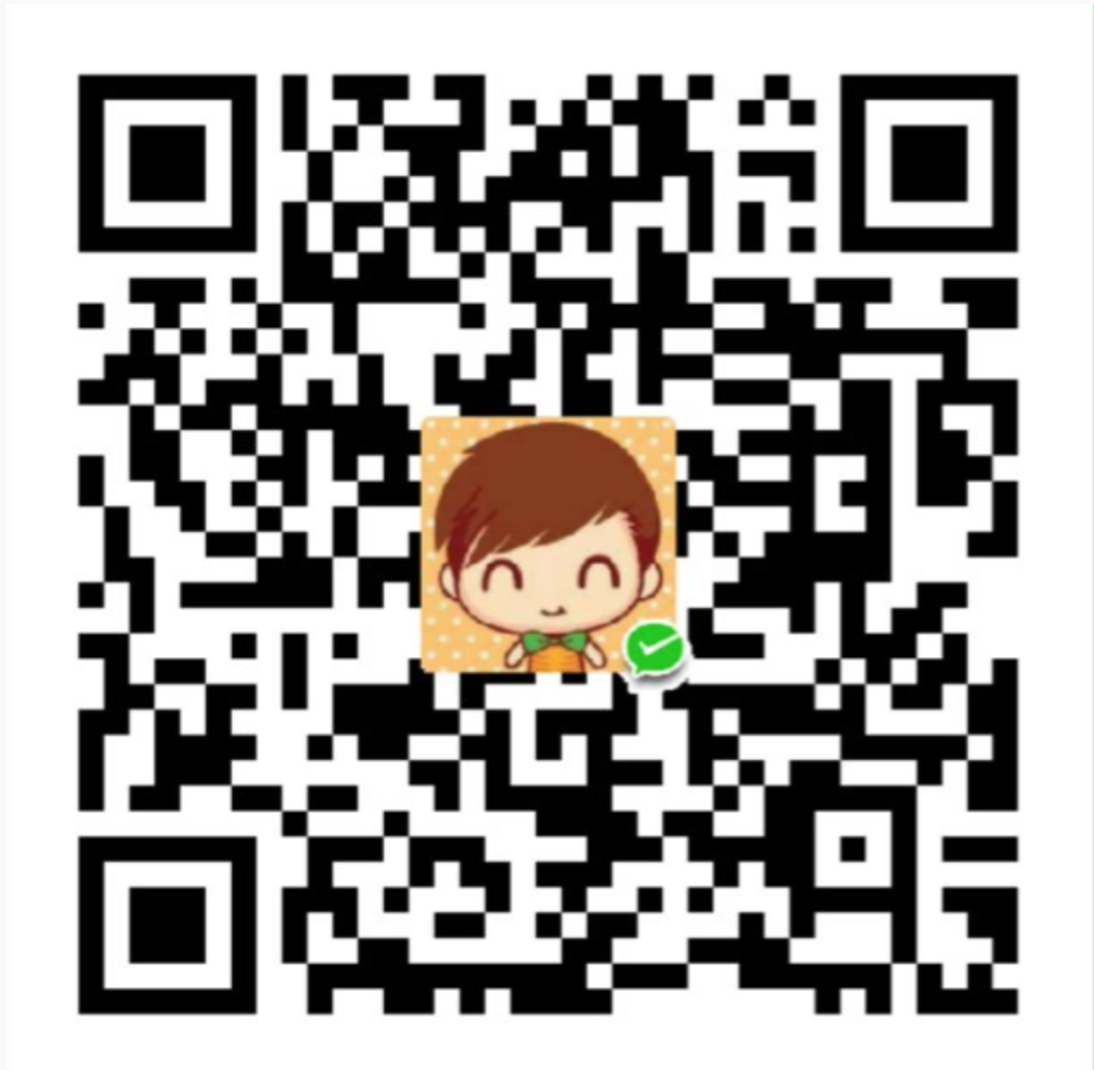
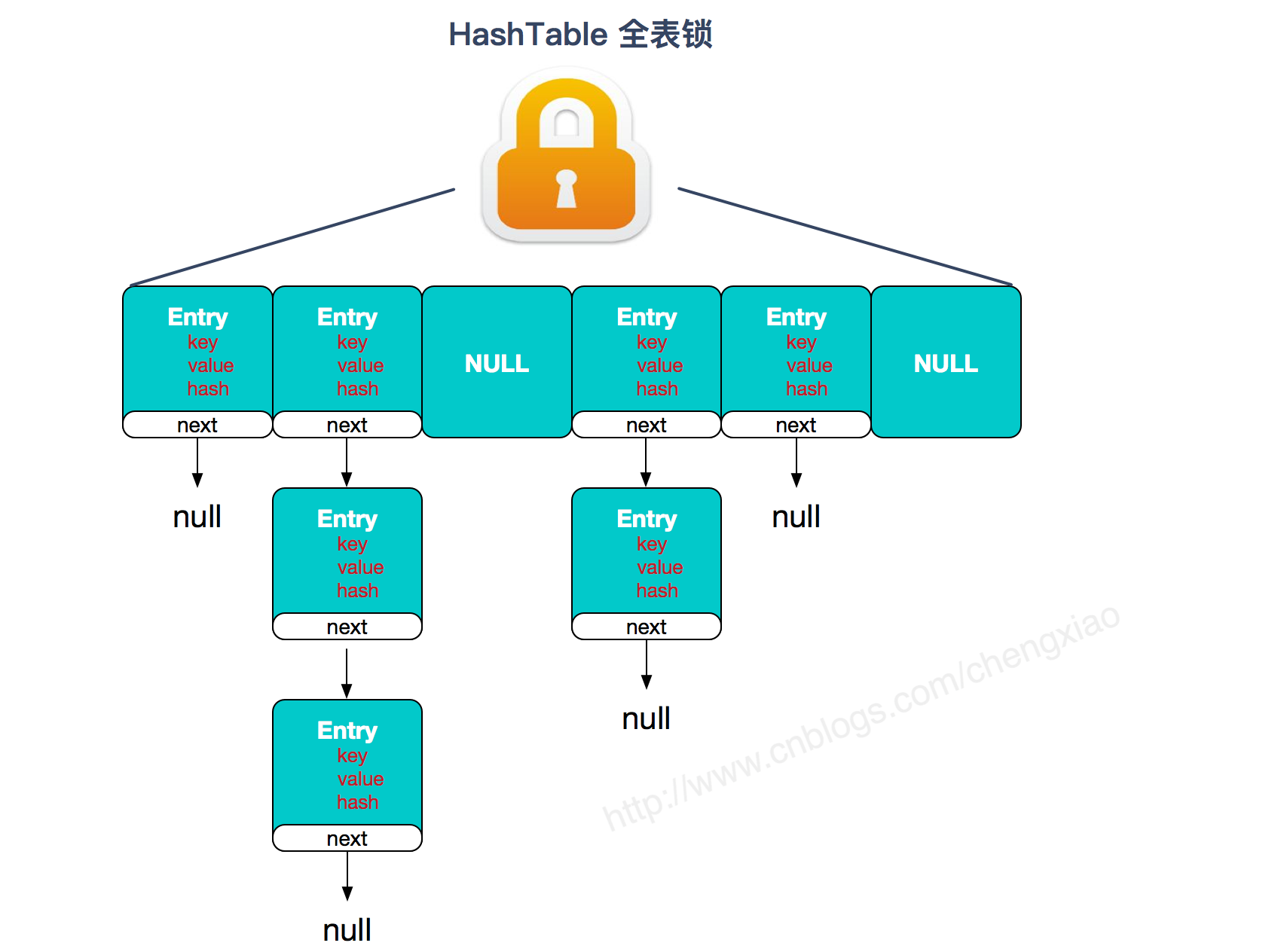
Hashtable原理
Hashtable(同一把锁) :使用 synchronized 来保证线程安全,效率非常低下。当一个线程访问同步方法时,其他线程也访问同步方法,可能会进入阻塞或轮询状态,如使用 put 添加元素,另一个线程不能使用 put 添加元素,也不能使用 get,竞争会越来越激烈效率越低。
JDK1.7 ConcurrentHashMap
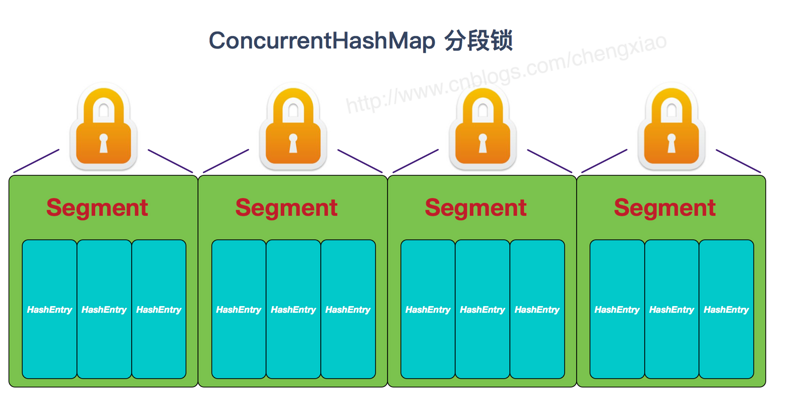
首先将数据分为一段一段的存储,然后给每一段数据配一把锁,当一个线程占用锁访问其中一个段数据时,其他段的数据也能被其他线程访问。
ConcurrentHashMap 是由 Segment 数组结构和 HahEntry 数组结构组成。
Segment 实现了 ReentrantLock,所以 Segment 是一种可重入锁,扮演锁的角色。HashEntry 用于存储键值对数据。
1
| static class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable
|
一个 ConcurrentHashMap 里包含一个 Segment 数组。Segment 的结构和HashMap类似,是一种数组和链表结构,一个 Segment 包含一个 HashEntry 数组,每个 HashEntry 是一个链表结构的元素,每个 Segment 守护着一个HashEntry数组里的元素,当对 HashEntry 数组的数据进行修改时,必须首先获得对应的 Segment的锁。
JDK1.8 ConcurrentHashMap
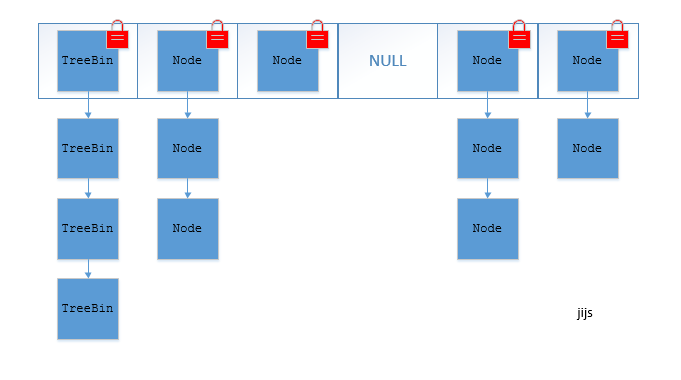
ConcurrentHashMap取消了Segment分段锁,采用CAS和synchronized来保证并发安全。数据结构跟HashMap1.8的结构类似,数组+链表/红黑二叉树。
synchronized只锁定当前链表或红黑二叉树的首节点,这样只要hash不冲突,就不会产生并发,效率又提升N倍。(jdk1.7 segment 数组不能扩容,扩容是 segment 数组某个位置内部的数组 HashEntry[] 进行扩容)
put源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break;
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
|
put解析
根据哈希值算出位置i,空位直接放入,CAS不用加锁, 链表插末尾, 树节点, 按树的方式插入。
ConcurrentHashMap不允许key或value为空。
JDK8的ConcurrentHashMap实现只锁住Node,锁粒度更细。并且只对改冲突链加锁,之前的操作都是无锁且线程安全的。
多线程实现:
如果检测到其它线程正在为其扩容(检测到被插入的位置被forward节点占有),当前put方法的线程也要参与到扩容中去。
检测到节点位置为空,直接放入,检测到节点非空且不是foward节点,加锁重构链表或树。加入链表后节点长度大于8,要转为红黑树。(扩容后也可能再降回链表)
JDK8实现的ConcurrentHashMap总结:
JDK7的实现用Segment减小锁粒度,分段。put时仅锁住Segment。get时不加锁,仅用volatile保证可见性。统计size用两次尝试的办法,不一致再加锁。主要问题是冲突链表的增删改查耗时长。
JDK8的设计优化:
- 直接锁住Node,减小了锁粒度。
- 设计了MOVED状态,使其它put线程协助扩容。
- 3个CAS操作保证线程安全,用更轻量的方式替代了锁。
- sizeCtl扩容控制符。
- 足够信作synchronized,不再使用ReentrantLock
get源码
get 方法可以根据指定的键,返回对应的键值对,由于是读操作,所以不涉及到并发问题.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
|



